Research Metrics¶
Journals¶
Impact Factor¶
Are the number of citations received per paper published in the journal in the two preceeding years. It was introduced by Eugene Garfield of the for Scientific Information and has been calculated since 1975.
It’s unfortunately fallible, due to self citations, causing the journals to be able to bulk up their own ranking. Thomson Reuters did a big cull of self citing journals, 140 of which had more than 70% of their citations being internal. For comparison, ⅘ journals keep these self citations below 30%
Eigenfactor¶
An alternate measure of journal impact was developed, called the eigenfactor, which has a scaling factor for the source of the citations, so citations coming form more influential journals would mean more than citations from less influential ones
Researchers¶
Researcher identifiers are used to trace publications, track citations and calculate researcher metrics, they can also be used to identify collaborators and is integrated with the web of science to build a network of how researchers work together.
There are multiple different metrics, such as:
- h-index
- Number of downloads
- ‘Universal citation impact measure’ (extends h-index)
- ‘Automated citation indexing’ through google scholar
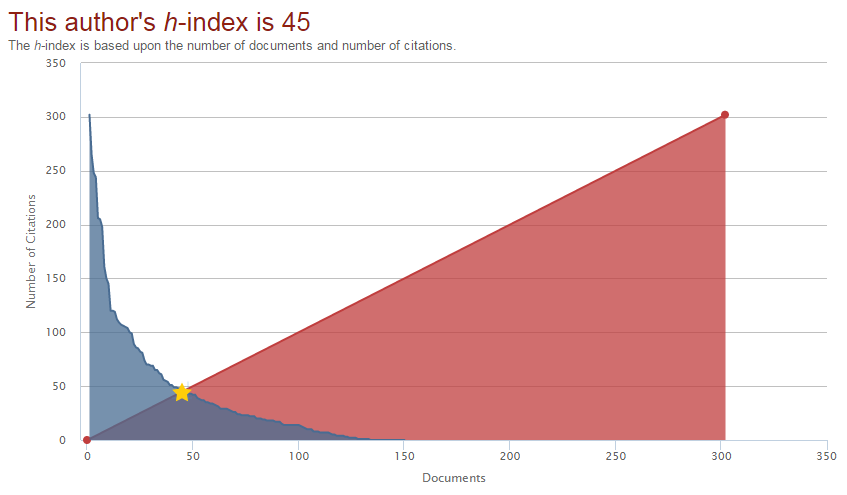
h-index¶
Introduced by Jorge E. Hirsch, the h-index is the total number of citations for an author’s papers that have been cited that many times, as shown in the plot below. This can be measured for an individual, a group, an institution, a country, etc.
This does have a few flaws, however, as there can be many authors of a paper, and it very much preferentially serves experimental research over theoretical research. It also doesn’t scale itself for the amount of citations that each field will typically see and is fundamentally proportional to the longevity of the researcher’s career. There’s also disparities between book citations and journal citations, and it doesn’t account for the context in which the citation occurs (it could be a citation criticising the work).
Institutions¶
Academic Rankings¶
There are many different metrics that are used to rank institutions, most of which use bibliometrics as a basis, including Essential Science Indicators, Web of Science, Scopus and Webometrics Ranking of World Universities.
Shanghai Jiao Tang University (SJTO) Parameters¶
Are a set of metrics that can be used to measure the output of a university:
| Parameter | Weighting (%) |
|---|---|
| Number of articles published in Nature or Science | 20 |
| Number of highly cited researchers in 21 broad subject categories | 20 |
| Academic performance with respect to size of institution | 10 |
| Number of staff and alumni of the institution winning Nobel Prize and Fields Medals | 20 |
| Articles in Science Citation Index-expanded, Social Science Citation Index, and Arts and Humanities Citation Index | 30 |
University Rankings¶
Rank all the academic institutions in the world based on a set of indicators in five broad faculty areas:
- Arts & Humanities
- Engineering & Technology
- Life Sciences & Medicine
- Natural Sciences
- Social Sciences & Management
The parameters include:
- Overall rank and score
- Classifications
- Academic reputation (rank and score)
- Employer reputation (rank and score)
- Faculty student (rank and score)
- Citations per faculty (rank and score)
- International faculty (rank and score)
Excellence in Research for Australia (ERA)¶
Is awarded by the ARC, based on field of research (FoR) codes for each institution. They monitor ~23,000 journals and look for institutions with peer or editorial reviewed content with an ISSN .
The ERA have the following objectives:
- Establish an evaluation framework that gives government, industry, business and the wider community assurance of the excellence of research conducted in Australian higher education institutions
- Provide a national stocktake of discipline level areas of research strength and areas where there is opportunity for development in Australian higher education institutions
- Identify excellence across the full spectrum of research performance
- Identify emerging research areas and opportunities for further development
- Allow for comparisons of research in Australia, nationally and internationally, for all discipline areas.